RabbitMQ 的四种交换机
RabbitMQ 作为一个消息队列提供一个通用的消息发送和接收平台,并且保证消息在传输过程中的安全可靠。
消息 (Message) 由 Client 发送,RabbitMQ 接收到消息之后通过交换机转发到对应的队列上面。Worker 会从队列中获取未被读取的数据处理。
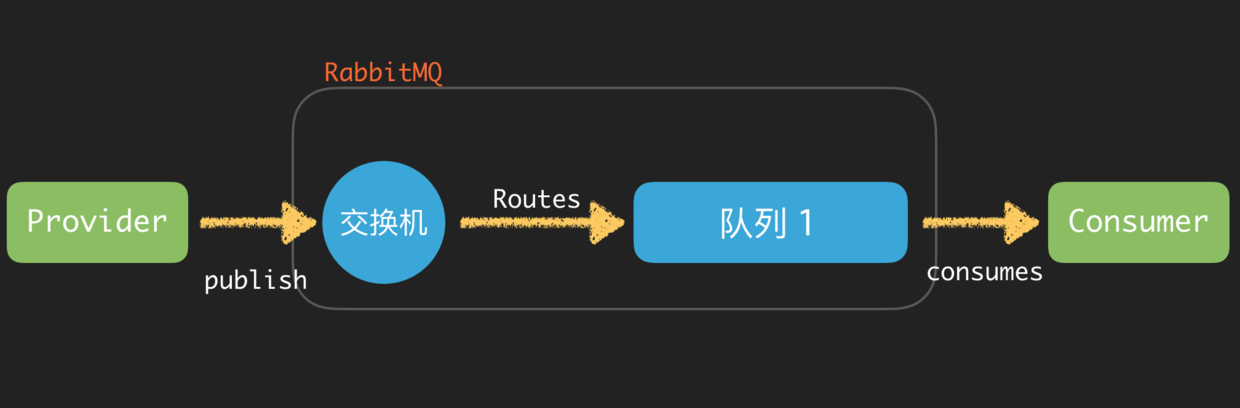
交换机
有 4 种不同的交换机类型:
直连交换机:Direct Exchange
扇形交换机:Fanout Exchange
主题交换机:Topic Exchange
首部交换机:Headers Exchange
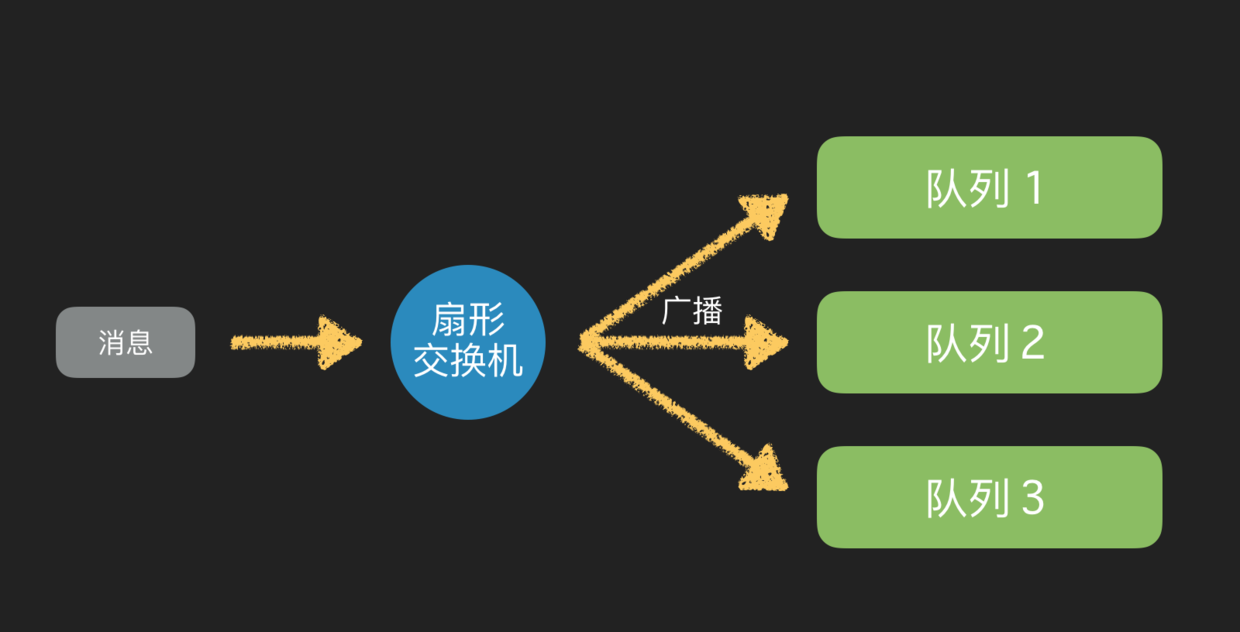
扇形交换机
扇形交换机是最基本的交换机类型,它所能做的事情非常简单———广播消息。扇形交换机会把能接收到的消息全部发送给绑定在自己身上的队列。因为广播不需要“思考”,所以扇形交换机处理消息的速度也是所有的交换机类型里面最快的。
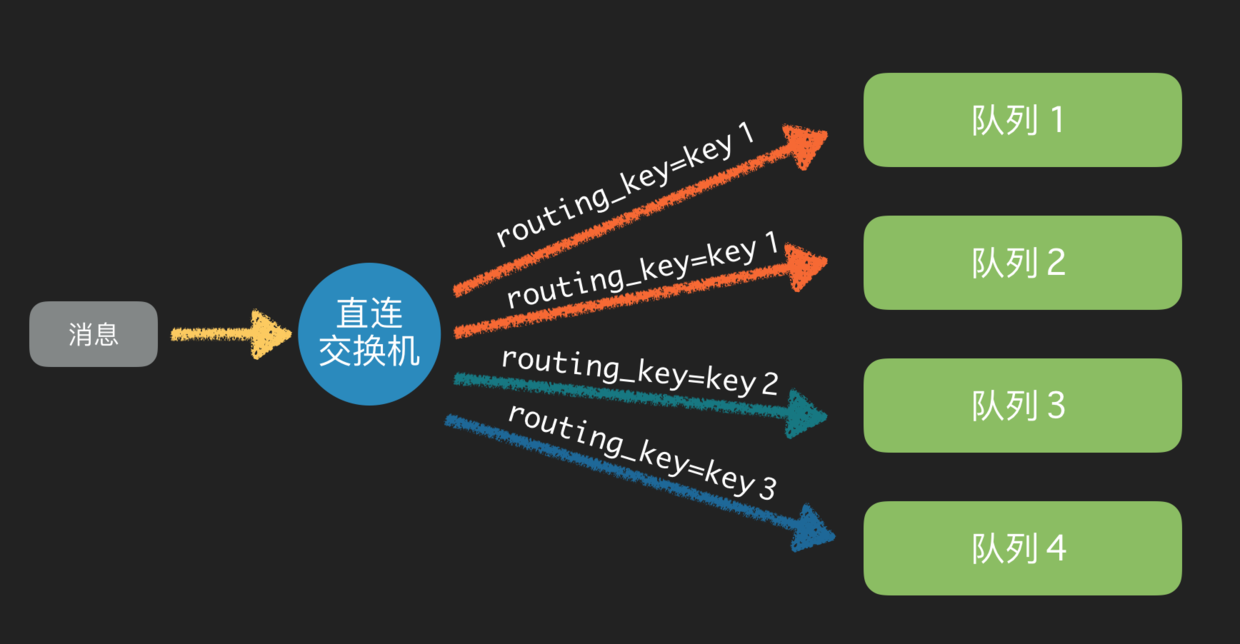
直连交换机
直连交换机是一种带路由功能的交换机,一个队列会和一个交换机绑定,除此之外再绑定一个 routing_key,当消息被发送的时候,需要指定一个 binding_key,这个消息被送达交换机的时候,就会被这个交换机送到指定的队列里面去。同样的一个 binding_key 也是支持应用到多个队列中的。
这样当一个交换机绑定多个队列,就会被送到对应的队列去处理。
适用场景:有优先级的任务,根据任务的优先级把消息发送到对应的队列,这样可以指派更多的资源去处理高优先级的队列。
主题交换机
直连交换机的 routing_key 方案非常简单,如果我们希望一条消息发送给多个队列,那么这个交换机需要绑定上非常多的 routing_key,假设每个交换机上都绑定一堆的 routing_key 连接到各个队列上。那么消息的管理就会异常地困难。
所以 RabbitMQ 提供了一种主题交换机,发送到主题交换机上的消息需要携带指定规则的 routing_key,主题交换机会根据这个规则将数据发送到对应的(多个)队列上。
主题交换机的 routing_key 需要有一定的规则,交换机和队列的 binding_key 需要采用 *.#.*..... 的格式,每个部分用 . 分开,其中:
*表示一个单词#表示任意数量(零个或多个)单词。
假设有一条消息的 routing_key 为 fast.rabbit.white,那么带有这样 binding_key 的几个队列都会接收这条消息:
- fast..
- ..white
- fast.#
- ……
这个图是网上找的,感觉对主题交换机的描述比较到位:
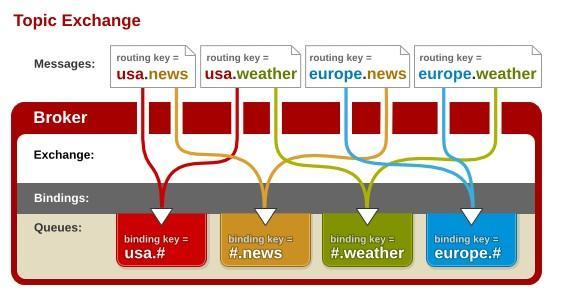
当一个队列的绑定键为 # 的时候,这个队列将会无视消息的路由键,接收所有的消息。
首部交换机
首部交换机是忽略 routing_key 的一种路由方式。路由器和交换机路由的规则是通过 Headers 信息来交换的,这个有点像 HTTP 的 Headers。将一个交换机声明成首部交换机,绑定一个队列的时候,定义一个 Hash 的数据结构,消息发送的时候,会携带一组 hash 数据结构的信息,当 Hash 的内容匹配上的时候,消息就会被写入队列。
绑定交换机和队列的时候,Hash 结构中要求携带一个键“x-match”,这个键的 Value 可以是 any 或者 all,这代表消息携带的Hash是需要全部匹配(all),还是仅匹配一个键(any)就可以了。相比直连交换机,首部交换机的优势是匹配的规则不被限定为字符串(string)。
Spring Boot 中的实例
推荐在 Docker 中安装运行 RabbitMQ,非常方便。
配置
pom.xml
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency>
application.properties
#rabbitmqspring.rabbitmq.host=localhostspring.rabbitmq.port=5672spring.rabbitmq.username=guestspring.rabbitmq.password=guestspring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/#消费者spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.concurrency=10spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.max-concurrency=10#从队列中每次取x个spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.prefetch=1#消费者自动启动spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.auto-startup=true# 重试spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.default-requeue-rejected=true#发送者spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.enabled=truespring.rabbitmq.template.retry.initial-interval=1000spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.max-attempts=3spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.max-interval=10000spring.rabbitmq.template.retry.multiplier=1.0
直连交换机
配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;/*** 最新版本的RabbitMQ有四种交换机类型,分别是Direct exchange、Fanout exchange、Topic exchange、Headers exchange。*/@Configurationpublic class MQConfig {public static final String QUEUE = "queue";@Beanpublic Queue queue() {return new Queue(QUEUE, true);}}
默认的交换机为直连交换机,也可以显式指定直连交换机
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;@Configurationpublic class MQConfig {public static final String QUEUE = "queue";public static final String DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "directExchage";@Beanpublic Queue queue() {return new Queue(QUEUE, true);}/*** direct模式* 一个队列会和一个交换机绑定,除此之外再绑定一个routing_key。*/@Beanpublic DirectExchange directExchange(){return new DirectExchange(DIRECT_EXCHANGE);}@Beanpublic Binding topicBinding() {return BindingBuilder.bind(queue()).to(directExchange()).with("key");}}
发送者
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQSender {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate ;public void send(Object message) {System.out.println("send message:" + message.toString());amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.QUEUE, message.toString());}}
如果采用了显式指定直连交换机则需要按照下面的方法来发送消息
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQSender {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate ;public void sendDirect(Object message) {System.out.println("send direct message:" + message.toString());amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "key", message.toString());}}
接收者
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQReceiver {@RabbitListener(queues=MQConfig.QUEUE)public void receive(String message) {System.out.println("receive direct message:" + message);}}
主题交换机
配置类
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;@Configurationpublic class MQConfig {public static final String QUEUE1 = "queue1";public static final String QUEUE2 = "queue2";public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "topicExchage";@Beanpublic Queue queue1() {return new Queue(QUEUE1, true);}@Beanpublic Queue queue2() {return new Queue(QUEUE2, true);}/*** Topic模式 交换机Exchange* 先放入交换机中,通过with里参数筛选后再放入queue中。* 直连交换机的routing_key方案非常简单,如果我们希望一条消息发送给多个队列,* 那么这个交换机需要绑定上非常多的routing_key,* 假设每个交换机上都绑定一堆的routing_key连接到各个队列上。那么消息的管理就会异常地困难。* 所以RabbitMQ提供了一种主题交换机,发送到主题交换机上的消息需要携带指定规则的routing_key,* 主题交换机会根据这个规则将数据发送到对应的(多个)队列上。* 主题交换机支持通配符,* 代表一个字符,# 代表0个或多个字符* */@Beanpublic TopicExchange topicExchange(){return new TopicExchange(TOPIC_EXCHANGE);}@Beanpublic Binding topicBinding1() {return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.key1");}@Beanpublic Binding topicBinding2() {return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.#");}}
发送者
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQSender {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate ;public void sendTopic(Object message) {System.out.println("send topic message:" + message.toString());amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "topic.key1", "第1条消息:" + message.toString());amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "topic.key2", "第2条消息:" + message.toString());}}
接收者
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQReceiver {@RabbitListener(queues=MQConfig.QUEUE1)public void receiveQueue1(String message) {System.out.println("receive queue1 message:" + message);}@RabbitListener(queues=MQConfig.QUEUE2)public void receiveQueue2(String message) {System.out.println("receive queue2 message:" + message);}}
扇形交换机
配置类
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;@Configurationpublic class MQConfig {public static final String QUEUE1 = "queue1";public static final String QUEUE2 = "queue2";public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "topicExchage";@Beanpublic Queue queue1() {return new Queue(QUEUE1, true);}@Beanpublic Queue queue2() {return new Queue(QUEUE2, true);}/*** Fanout模式 交换机Exchange* 先放入交换机中,不需要通过筛选,所有绑定的queue都能接收到。* */@Beanpublic FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){return new FanoutExchange(FANOUT_EXCHANGE);}@Beanpublic Binding FanoutBinding1() {return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(fanoutExchange());}@Beanpublic Binding FanoutBinding2() {return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(fanoutExchange());}}
发送者
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQSender {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate ;public void sendFanout(Object message) {System.out.println("send fanout message:" + message.toString());amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", message.toString());}}
接收者
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQReceiver {@RabbitListener(queues=MQConfig.QUEUE1)public void receiveQueue1(String message) {System.out.println("receive queue1 message:" + message);}@RabbitListener(queues=MQConfig.QUEUE2)public void receiveQueue2(String message) {System.out.println("receive queue2 message:" + message);}}
首部交换机
配置类
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;import org.springframework.amqp.core.HeadersExchange;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;@Configurationpublic class MQConfig {public static final String HEADERS_QUEUE = "headers.queue";public static final String HEADERS_EXCHANGE = "headersExchage";@Beanpublic Queue headersQueue() {return new Queue(HEADERS_QUEUE, true);}/*** Header模式 交换机Exchange* 首部交换机是忽略routing_key的一种路由方式。* 路由器和交换机路由的规则是通过Headers信息来交换的,这个有点像HTTP的Headers。* 将一个交换机声明成首部交换机,绑定一个队列的时候,定义一个Hash的数据结构,* 消息发送的时候,会携带一组hash数据结构的信息,当Hash的内容匹配上的时候,消息就会被写入队列。* 绑定交换机和队列的时候,Hash结构中要求携带一个键“x-match”,这个键的Value可以是any或者all,* 这代表消息携带的Hash是需要全部匹配(all),还是仅匹配一个键(any)就可以了。* 相比直连交换机,首部交换机的优势是匹配的规则不被限定为字符串(string)。* */@Beanpublic HeadersExchange headersExchange(){return new HeadersExchange(HEADERS_EXCHANGE);}@Beanpublic Binding headersBinding() {Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();map.put("header1", "value1");map.put("header2", "value2");//whereAll,whereAny,whereOne等等,有许多条件,含义参看文档return BindingBuilder.bind(headersQueue1()).to(headersExchange()).whereAll(map).match();}}
发送者
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageProperties;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQSender {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate ;public void sendHeaders(Object message) {System.out.println("send headers message:" + message.toString());MessageProperties properties = new MessageProperties();properties.setHeader("header1", "value1");properties.setHeader("header2", "value2");Message obj = new Message(msg.getBytes(), properties);amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.HEADERS_EXCHANGE, "", obj);}}
接收者
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Servicepublic class MQReceiver {@RabbitListener(queues=MQConfig.HEADERS_QUEUE)public void receiveHeaderQueue(byte[] message) {System.out.println("receive headers queue message:" + new String(message));}}
评论